THC is the chemical in marijuana that causes it to get users high. It’s a potent stuff that can have a big influence on both your body and mind.
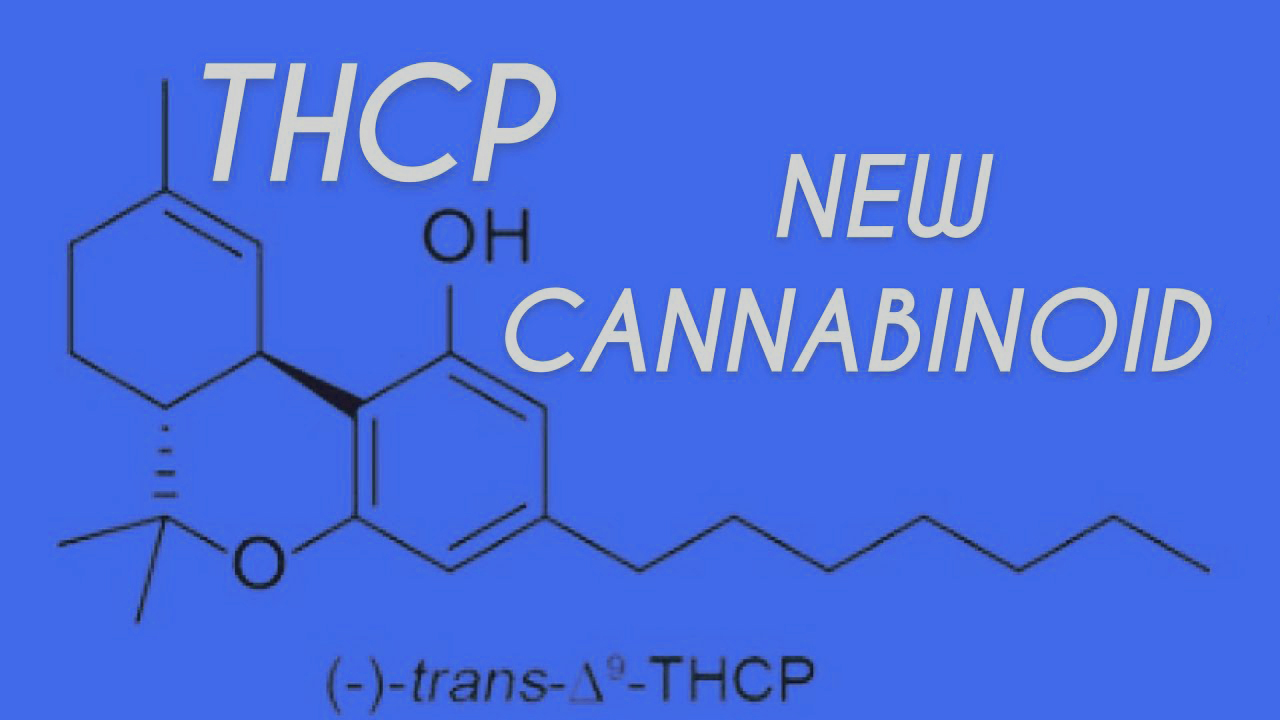
The scientific journal Scientific Reports has published a groundbreaking finding of a previously unknown cannabinoid. THCP is a unique cannabinoid that was given this name because it had not been seen previously. It’s also unclear how psychoactive it is in humans or which cannabis strains contain it, but it appears to be considerably more potent than THC.
Humans have been using cannabis’ intoxicating effects for thousands of years, but it’s only recently that researchers discovered how the plant causes its psychotropic effects. In the late 1980s, scientists found a new type of brain receptor that responds directly to compounds in cannabis. A few years later, a second similar receptor was discovered, and they were dubbed CB1 and CB2.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) activates these two types of receptors, which are present in high amounts throughout the body. Perhaps the most well-known psychoactive component in cannabis, THC binds strongly to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Endocannabinoids, a group of naturally occurring neurotransmitters that interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors, are another type of neurotransmitter that interacts with cannabinoid receptors.
New Cannabinoids Discovered
In the December 30th, 2019 issue of Scientific Reports, a group of Italian researchers officially unveiled the new cannabinoids THCP and CDBP to the scientific community. The team discovered two distinct organic molecules that were almost identical in structure to THC and CBD, with one big difference.
Cannabinoids come in a variety of forms, each with its own characteristic set of chemical bonds. Cannabinoids have alkyl side chains, which are made up of a string of carbon atoms. These side chains attach to CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain, allowing cannabinoids to produce significant changes in neural activity.
THC and CBD molecules, like other cannabinoids, include five carbon atoms in their alkyl side chains. Synthetic cannabinoids with longer chains have been developed previously, but it wasn’t clear if Cannabis sativa plants could create organic compounds with this structure.
This has been confirmed. The Italian researchers found THC and CBD analogs with seven carbon atoms in their alkyl side chains while studying samples from a strain of medicinal cannabis known as FM2, which was provided by the Military Chemical Institute in Florence. It had already been discovered that longer side chains would bind more firmly and actively to CB1 and CB2 neurochemical docking sites in the brain’s endocannabinoid system, resulting in a stronger brain response to such chemicals.
In further in vitro analysis, the researchers discovered that THCP and CBDP acted similarly to enhanced versions of THC and CBD. Since the therapeutic effects and mind-altering powers of THC are well known, the scientists were interested in learning more about THCP. THCP has a binding affinity for CB1 receptors 33 times greater than THC, indicating that its effects in the brain may be considerably more significant. THC’s medical efficacy and potency have already been praised by doctors and patients, which bodes well for THCP as a medicinal component.
Is THCP Already Helping Patients?
Cannabis is a significant source of revenue for the pharmaceutical industry. Medicinal cannabis goods are notorious for their unpredictability. From person to person and even from use to use, outcomes differ.
The researchers note that the recent study has uncovered a new and distinct cannabinoid receptor that may play an important role in health and disease. “This chemical,” they write, should be included on the list of important phytocannabinoids to be studied for a correct assessment of the pharmacological effect of cannabis extracts given to patients. We think that the discovery of an extremely potent THC-like phytocannabinoid may provide insight into several pharmacological effects that can’t be explained by THC alone.”
Even if THCP is only present in trace amounts in a few distinct strains, selective breeding and genetic selection might produce new strains with higher levels of THC. For illnesses or disorders for which THC has been found to be beneficial, extracts high in THCP may be used to create medicines.
To date, around 150 cannabinoids have been discovered in different Cannabis sativa strains. The possibility that many more may be found in the years to come as research techniques improve is open through this latest study, similar to others like it before it.
It’s conceivable, if not very likely, that the therapeutic or mind-altering effects attributed to THC, CBD, and other already identified cannabinoids may be linked to the activity of these yet unknown chemicals. Some of these chemicals may be just as potent, if not more so, than THCP appears to be; however, this is just speculation for now.
The Future of THCP
The most common application for THC-based medical cannabis is the treatment of chronic pain. Because their chemical structures are comparable, it’s probable that THPC is more effective at reducing pain than products containing substantial amounts of THC. If this is true, medicines produced to contain large quantities of THPC could potentially become a superior option to opioids, which are more addicting and sometimes deadly than cannabis-based medications.
In the United States, between 40,000 and 50,000 people will die of an opioid overdose every year. This demonstrates just how serious the opioid epidemic is, as well as the importance of developing alternative strong painkillers to replace these harmful drugs.
The discovery of THCP is still relatively recent, and scientists are still learning about its characteristics and capabilities. In the meantime, other new cannabinoids continue to be sought after. Medicinal cannabis has only been around for a few decades on the American healthcare scene, and the Cannabis sativa plant continues to hide many secrets. It isn’t ridiculous to believe that cannabis may eventually revolutionize medical treatment once its mysteries have been unlocked considering what has already been learnt.
What Is THCP?
THCP is a phytocannabinoid, one of the hundreds of active compounds discovered in cannabis plants’ resinous trichomes. Researchers have discovered approximately 150 distinct chemicals thus far, and THCP is one of them. Cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids are all valuable components found in cannabis. Cannabinoids, on the other hand, have received a great deal of attention for their therapeutic benefits.
There are many different cannabinoids with various properties. Some of the best-known examples include:
- Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
Let’s look at how cannabis plants synthesize these cannabinoids and what makes them so special.
How Cannabis Plants Produce THCP
There are many different phytocannabinoids, but they all have a similar chemical structure. This is due to the fact that they all start out as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), which is a precursor to THC and CBD.
Many individuals call CBGA “the mother cannabinoid.” It is created via a complicated chemical reaction between olivetolic acid and geranyl pyrophosphate. It then goes through enzymatic transformations to produce the acidic phytocannabinoids: THCA, CBDA, and CBCA, among others.
Raw cannabis only contains acidic cannabinoids in its unaltered form. When they come into contact with heat, decarboxylation occurs, a process that transforms THCA to THC, CBDA to CBD, and CBCA to CBC. After being subjected to heat, these phytocannabinoids change into similar phytocannabinoids. nTHCPA and CBDPA develop similarly to the other phytocannabinoids.
THCP and CBDP, on the other hand, are much more rare. They have thus remained undiscovered until now because they exist in such low amounts in marijuana plants as compared to THCV or CBN.
How Is THCP Different from THC?
THC and THCP have very similar chemical structures. The distinction is in their ‘side alkyl chain.’ nAn alkyl chain is a group of carbon and hydrogen atoms linked to a molecule. THC has an alkyl chain with five carbon atoms. THCP, on the other hand, has a seven-carbon side chain. It’s this difference in the length of the alkyl chain that influences the chemical’s effect. It appears that having more carbon atoms in its side chain improves THCP’s potency dramatically over THC.
Carbon Chains and Cannabinoids: Size Matters
The length of the alkyl chains in all cannabinoids is rather similar, although they can vary. THCA, CBDA, and CBCA have five carbon atoms in their alkyl chains. THCV and CBDV have chains with just three carbon atoms. THC-C1 and CBD-C1 are two examples of cannabinoids with chains containing only a single carbon atom. ‘Varinoids’ are those that contain five-carbon alkyl chain s. ‘Orchinoids,’ on the other hand, refers to chemicals with three-carbon alkyl chain s
Some studies suggest that phytocannabinoids with longer alkyl chains bind more readily to cannabinoid receptors in the body. Synthetic cannabinoids with alkyl chains greater than five carbon atoms have far greater potency than THC, for example. The most potent effects are produced by chemicals with eight carbon chain alkyl groups. If the chain length is greater than 8 carbons, it begins to lose its effectiveness.
The mechanism by which phytocannabinoids bind to body receptors explains why this is the case. The endocannabinoid system’s CB1 and CB2 receptors are a crucial component (ECS). Cannabinoids’ ability to bind with these receptors improves as a result of longer alkyl chains. This is due to the fact that THCP’s seven-carbon chain enables it to interact better with these receptors, increasing its impact.
THCP Benefits and Risks
To assess the recently discovered THCP, Citti et al. conducted a study on mice. The researchers identified that when low dosages of 2.5mg/kg were fed to the animals, they became less active. When dosages of 5mg/kg and 10mg/kg were used, the sedative effects of the chemical increased significantly. The mice went into a cataleptic state in which their bodies became rigid and immobile, according to Citti et al. THCP also exhibited significant painkilling properties at these doses, according to Citti et al.
According to the researchers, THCP may be responsible for some marijuana strains’ pharmacological effects. However, it appears that the advantages of THCP are dose-dependent. Despite this, the team did not test THCP on humans.
The worry of adverse effects is one deterrent that keeps individuals from utilizing high-THC cannabis for medical purposes. Dry mouth, drowsiness, anxiety, paranoia, and dizziness are just a few examples of typical symptoms. THCP’s stronger nature might potentially exacerbate any of these negative side effects. As a result, it would be necessary to take great care with dosage and monitoring in order to obtain meaningful results.
How Much THCP Is in Cannabis?
THCP and CBDP are less plentiful than THC and CBD. For example, the Italian FM2 strain has the following typical ratios of the four cannabinoids:
- THC: 39mg/g
- THCP: 29mcg/g
- CBD: 56mg/g
- CBDP: 243mcg/g
Keep in mind that the measurements for THC, CBD, THCP, and CBDP are all in milligrams, while the figures for THCP and CBDP are in micrograms. The concentrations of these newly discovered cannabinoids are quite low; no wonder they have gone unnoticed by researchers for so long! We currently know very little about the THCP content of other cannabis strains. However, this information should be readily available as research into cannabinoids continues.
The two cannabinoids THCV and CBDP are a pair of phytocannabinoids that have been hidden until now. According to early studies, they may be up to 100 times more powerful than THC and CBD. As a result of this fascinating discovery, we could utilize cannabis in a very different way in the future.
Overall, we still have a lot to learn about THCP and how it affects the body. We will gain a better understanding of this new chemical and how it may benefit medical cannabis patients as additional research is completed. If you want more information on medical marijuana or need an evaluation for medical marijuana certification, get in touch with us right away!
The development of pesticides out of natural compounds has been a time-tested approach to disease prevention. However, while these chemicals have significant medical benefits, they may also cause undesirable effects. More study is needed to determine their full impact on human health, therefore keep an eye on this space. We’ll provide more THCP and CBDP information as it becomes available.