Despite its youth as a research, THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is becoming more popular for its medicinal advantages. You’ve undoubtedly heard of THC, but have you heard of THCA? THCA is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in raw and living cannabis that isn’t intoxicating like THC. When the plant dries up, THCA transforms to THC over time. When smoking or vaping flowers, decarboxylation occurs because heat accelerates this conversion (decarboxylation).
The marijuana plant contains 113 distinct cannabinoids. There may be hundreds of other chemicals in addition to terpenes and flavonoids, according to experts. Cannabis’ illegal status, on the other hand, restricts research into its properties. We’re most familiar with THC and CBD because they’re generally the two most common cannabinoids.
It is tempting to believe that these are among the few cannabinoids with potential benefits. However, in reality, the limited research on other chemicals reveals a different picture. It appears that compounds found in cannabis and hemp perform better together than they do alone. The term “entourage effect” refers to this occurrence.
It’s also conceivable that each cannabinoid and terpene has its own function. There are a slew of non-intoxicating cannabinoids in cannabis, as well as several that may cause intoxication. Obviously, alone, there isn’t enough of any psychoactive cannabinoid present to elicit this response on its own.
THCA is one of the cannabinoids that is gaining attention. We explore it and see how it differs from THC in this article.
What Is THCA?
The chemical known as THC is probably familiar to everyone who knows anything about marijuana. It’s the molecule that produces the euphoric high that so many people enjoy. Breeders today strive to produce plants with as much THC as possible. What many individuals are unaware of is that while raw marijuana contains a lot of THC, it does so in incredibly tiny amounts.
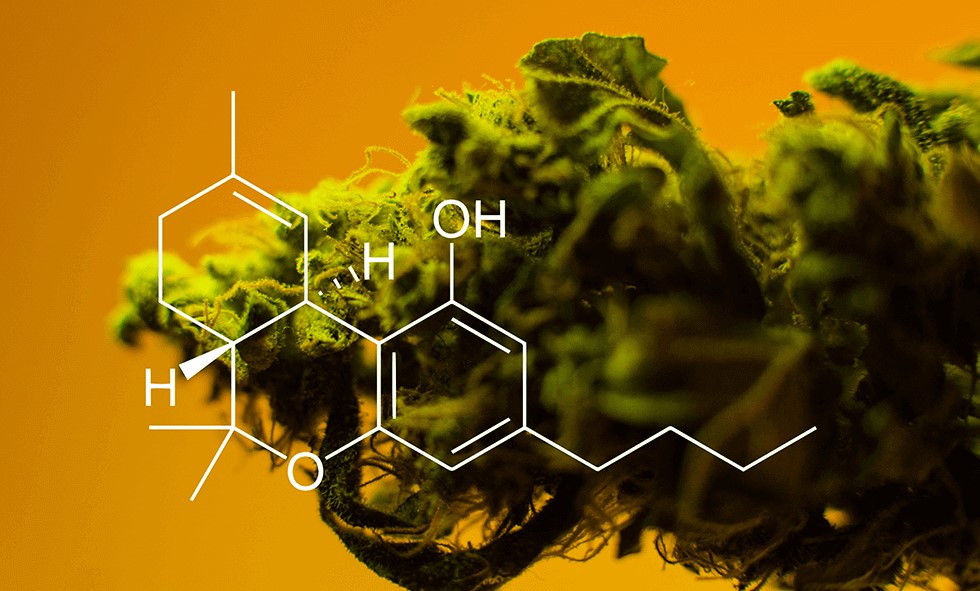
You may decarboxylate marijuana by subjecting it to heat. The act of vaporizing or smoking cannabis accomplishes this task automatically. Drying and curing the buds also helps you “decarb.” However, this technique takes a long time. THCA is the “precursor” acid to THC, while THC and THCA have many molecular similarities but minor differences in chemical structure. While they are nearly identical in terms of chemical make-up, they differ somewhat in structure.
THCV, on the other hand, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid present in raw cannabis plants. THCA, as mentioned before, does not generate any mind-altering effects. This is why you may theoretically consume a large quantity of raw marijuana buds without becoming intoxicated at all. THCA, on the other hand, has hundreds of therapeutic health advantages that it doesn’t produce an intoxicating high. It can help with pain relief (analgesic), inflammation reduction (anti-inflammatory), and brain protection (neuroprotective).
The chemical structure of THCA is almost the same as that of THC, with one important exception: it’s derived from CBGA. THCA, CBDA, and CBCA are three cannabinoid precursor chemicals produced by plants as they grow older.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THC) are two similar cannabinoids. However, because THCA is too big to fit into cannabinoid receptors, it is not suitable for those receptors in three-dimensional form. THC fits into your CB1 receptors as a result of which it induces intoxication. When THCA is heated to high temperatures (i.e., when you smoke or vaporize it), it transforms into THC. It creates a euphoric feeling at this point.
What Properties Does THCA Possess?
To begin with, it is necessary to make a disclaimer of sorts. There isn’t enough research on THCA to know what it can do. That said, the studies that have investigated cannabinoids have shown promise. It has been shown to act as a cannabinoid receptor and possess neuroprotective qualities in the laboratory setting.
Here’s a more thorough explanation of the characteristics associated with THCA, including its potential benefits. Keep in mind that there’s still a lot left to learn:
- Analgesic
- Antiemetic
- Neuroprotective
- Helps with insomnia
- Modulates the immune system
- Anti-inflammatory
There have been a few papers published on THCA’s potential health advantages. In 2011, researchers at Ruhaak et al. conducted a study in Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin that looked at six cannabinoids. The scientists wanted to see whether the cannabinoids had an anti-inflammatory effect. They discovered that THCA had anti-inflammatory capabilities.
Moldzio et al. studied THC and THCA in a study published in Phytomedicine in June 2012. According to the research, THCA may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
In July 2013, researchers from the American University of Beirut published a study in the British Journal of Pharmacology. THCA and CBDA were found to be useful in decreasing nausea and vomiting. To be sure, their effectiveness exceeded that of THC and CBD. The research was carried out on rodents, but it was still intriguing.
Recent research, on the other hand, has been nearly non-existent. Because scientists have a tough time obtaining money for THC and CBD research, it’s no surprise that there hasn’t been much recent study.
What are THCA’s Effects and Benefits?
There isn’t enough published research on THCA to determine what it can cure and with what degree of success, but preliminary study and anecdotal evidence suggest that the chemical will have a significant role in cannabis medicines as the industry grows. Here are some of the possible advantages studies are beginning to reveal:
- Anti-inflammatory properties for treatment of arthritis and lupus
- Neuroprotective properties for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
- Anti-emetic properties for treatment of nausea and appetite loss
- Anti-proliferative properties noted in studies of prostate cancer
Sleep disorders, muscular spasms, and pain are just a few of the other possible medicinal options promoted by patient accounts. Unfortunately, we’ll have to wait for further research to corroborate all of these advantages before we can fully comprehend what THCA stands for.
How Can I Use THCA?
How can you utilize THCA’s medical capabilities while avoiding smoking it and converting it to THC? Trimming raw cannabis buds and ‘juicing’ the plant material is one approach. We have a fantastic raw cannabis smoothie recipe on our site, which is a fast and easy method to get the most out of THCA.
The best way to consume it is as a tea. It’s also possible to decarboxylate THCA by steeping it in hot water and calling it THCA Tea. This procedure exposes the chemical to a modest temperature, preventing it from converting into THC. Other possibilities include sprinkling it on salads or making salad dressings with it.
It is important to note that the cannabis must not be exposed to a temperature greater than 250°F. This will happen if you do so. Dr. William Courtney of California’s Cannabis International group has a unique idea about this. He believes that raw cannabis contains 1,000 times more therapeutic cannabinoid acids (i.e., THCA) than its smoked or vaporized counterpart (see the graph above).
CBD oil, as well, has many of the same qualities as THC oil, according to study. It’s also non-intoxicating. Take a look at this article on CBD hemp oil for more information. Proponents maintain that it can aid with sleep, pain management, and anxiety relief.
Can You Smoke THCA?
The answer to this question is definitely ‘no,’ when THCA is exposed to heat. It is estimated that exposing THCA to a temperature of 212 degrees Fahrenheit for four hours would result in THC conversion completely. If you burn or vaporize raw marijuana, the THCA will be lost.
You now know that when THCA is smoked or vaped, it becomes THC. You’re also aware that after the plant has been dried and cured, the chemical change occurs more slowly. There are, however, numerous other ways in which decarboxylation may be achieved:
- Room Temperature: THCA is transformed into THC by being kept out in the open for long periods of time. In olive oil, exposing 22 percent of THCA to 77 degrees for ten days will result in a conversion rate of 22%. This proportion rises to 67 percent in an ethanol extraction. Even marijuana kept in a room with little light over many months will convert 20% THCA to THC.
- Sunlight: The general level of quality is the same. A lot is influenced by the overall temperature. When THCA molecules are exposed to ultraviolet radiation for an extended period of time, they change into THC.
- An Oven: Making cannabutter is one of the most popular methods of decarboxylating cannabis. Sprinkle the raw cannabis on a piece of parchment paper and put it in a preheated oven at 230°F for 30-90 minutes. Depending on the moisture level in the bud, activated THC may be produced in as little as 30 minutes. However, it might take anywhere from 90 to 90 minutes.
Why Do Dispensaries Label THCA Content?
Have you ever seen a strain’s strength assessed as THCA rather than THC? As a result, you must take it into account when determining a strain’s potency.
Gas chromatography is one of the most frequent ways to assess weed potency. The plant material you’re testing is heated with this approach. Cannabis is decarbed and its THCA is converted to THC using this method. The strength is measured in percentages, which gives us a clean and tidy number. At the very least, that’s the thinking behind it.
In reality, the weight of the cannabis decreases significantly during the heating and decarbing processes. This is due to a loss of carbonyl groups on THCA molecules. As a result, people may use this equation to test for THC:
THC = (% THCA) x (Final Mass/Initial Mass) + (% THC)
For others, the formula above represents a “safe” THC content. When you smoke marijuana, however, not all of the THCA converts to THC. To suggest that 30% THCA equals 30% THC is overly reductive. nWhen you smoke cannabis, only about 30% to 70 percent of any particular strain’s THCA is turned into THC.
When cannabis is raw, it contains a lot of THCA. When you decarboxylate it, this compound is changed to THC, the psychoactive cannabinoid that gives you a high. There isn’t much of a difference between the two in terms of molecule size. However, they have considerably different physiological and psychological effects on humans. THCA does not make you high.
Even if you don’t harm yourself or others, smoking raw marijuana might have a number of health advantages. Whether you want to learn more about this sort of marijuana is another question. Just bear in mind that heat exposure at high levels will ensure that the THCA is “removed” from the cannabis plant. You may create a raw weed smoothie or eat it as a leafy green to try THCA!